Kotlin/Wasm
Kotlin/Wasm has the power to compile your Kotlin code into WebAssembly (Wasm) format. With Kotlin/Wasm, you can create applications that run on different environments and devices, which support Wasm and meet Kotlin's requirements.
Wasm is a binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine. This format is platform-independent because it runs on its own virtual machine. Wasm provides Kotlin and other languages with a compilation target.
You can use Kotlin/Wasm in different target environments, such as browsers, for developing web applications built with Compose Multiplatform, or outside the browser in standalone Wasm virtual machines. In the outside-of-browser case, WebAssembly System Interface (WASI) provides access to platform APIs, which you can also utilize.
Kotlin/Wasm and Compose Multiplatform
With Kotlin, you have the power to build applications and reuse mobile and desktop user interfaces (UIs) in your web projects through Compose Multiplatform and Kotlin/Wasm.
Compose Multiplatform is a declarative framework based on Kotlin and Jetpack Compose that allows you to implement the UI once and share it across all the platforms you target.
For web platforms, Compose Multiplatform uses Kotlin/Wasm as its compilation target. Applications built with Kotlin/Wasm and Compose Multiplatform use a wasm-js target and run in browsers.
Explore our online demo of an application built with Compose Multiplatform and Kotlin/Wasm
Additionally, you can use the most popular Kotlin libraries in Kotlin/Wasm out of the box. Like in other Kotlin and Multiplatform projects, you can include dependency declarations in the build script. For more information, see Adding dependencies on multiplatform libraries.
Would you like to try it yourself?
Kotlin/Wasm and WASI
Kotlin/Wasm uses the WebAssembly System Interface (WASI) for server-side applications. Applications built with Kotlin/Wasm and WASI use a Wasm-WASI target, allowing you to call the WASI API and run applications outside the browser environment.
Kotlin/Wasm leverages WASI to abstract away platform-specific details, allowing the same Kotlin code to run across diverse platforms. This expands the reach of Kotlin/Wasm beyond web applications without requiring custom handling for each runtime.
WASI provides a secure standard interface for running Kotlin applications compiled to WebAssembly across different environments.
Kotlin/Wasm performance
Although Kotlin/Wasm is still in Beta, Compose Multiplatform running on Kotlin/Wasm already shows encouraging performance traits. You can see that its execution speed outperforms JavaScript and is approaching that of the JVM:
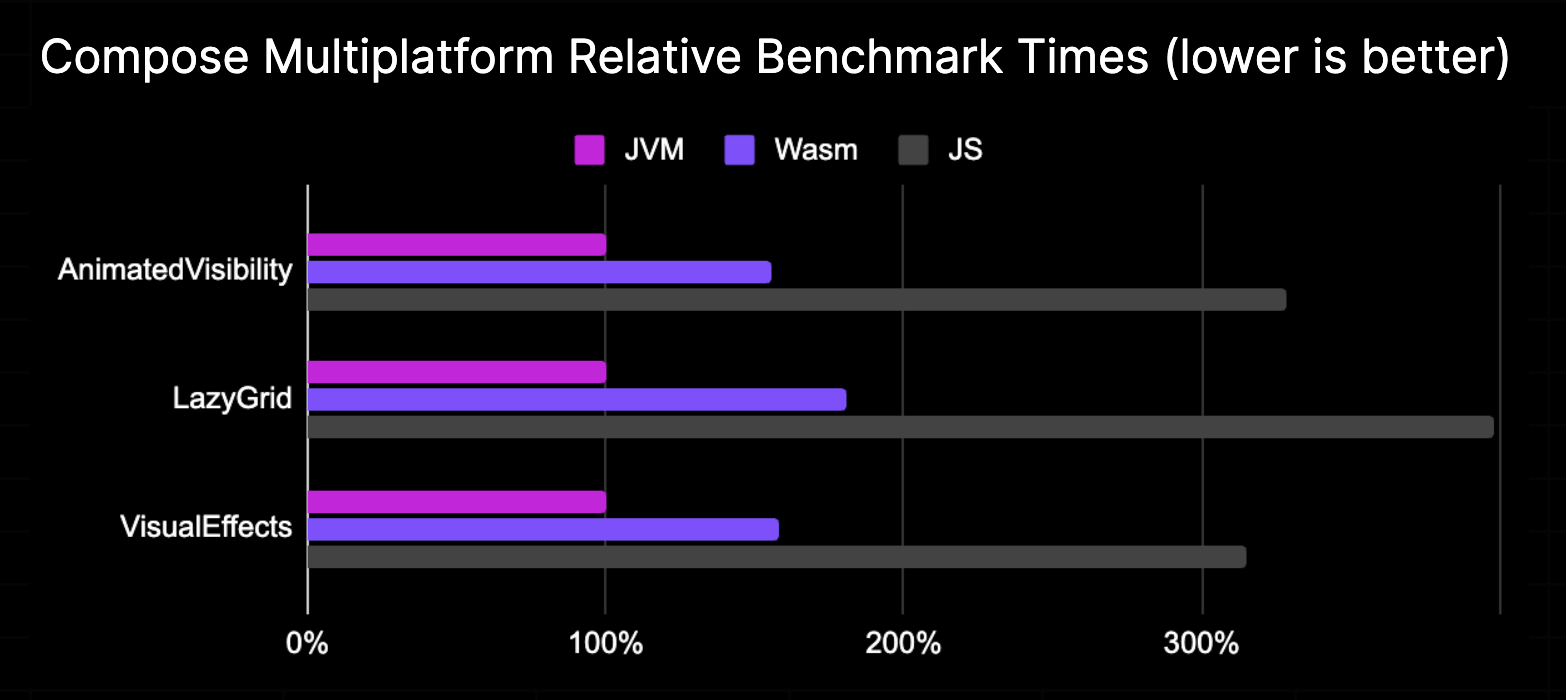
We regularly run benchmarks on Kotlin/Wasm, and these results come from our testing in a recent version of Google Chrome.
Browser API support
The Kotlin/Wasm standard library provides declarations for browser APIs, including the DOM API. With these declarations, you can directly use the Kotlin API to access and utilize various browser functionalities. For example, in your Kotlin/Wasm applications, you can use manipulation with DOM elements or fetch the API without defining these declarations from scratch. To learn more, see our Kotlin/Wasm browser example.
The declarations for browser API support are defined using JavaScript interoperability capabilities. You can use the same capabilities to define your own declarations. In addition, Kotlin/Wasm–JavaScript interoperability allows you to use Kotlin code from JavaScript. For more information, see Use Kotlin code in JavaScript.
Leave feedback
Kotlin/Wasm feedback
Slack: Get a Slack invite and provide your feedback directly to developers in our #webassembly channel.
Report any issues in YouTrack.
Compose Multiplatform feedback
Slack: provide your feedback in the #compose-web public channel.
Learn more
Learn more about Kotlin/Wasm in this YouTube playlist.
Explore the Kotlin/Wasm examples in our GitHub repository.