Test Java code using Kotlin and JUnit – tutorial
Kotlin is fully interoperable with Java, which means you can write tests for Java code using Kotlin and run them together with your existing Java tests in the same project.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to:
Configure a mixed Java–Kotlin project to run tests using JUnit.
Add Kotlin tests that verify Java code.
Run tests using Maven or Gradle.
Configure the project
In your IDE, clone the sample project from version control:
https://github.com/kotlin-hands-on/kotlin-junit-sample.gitNavigate to the
initialmodule and review the project structure:kotlin-junit-sample/ ├── initial/ │ ├── src/ │ │ ├── main/java/ # Java source code │ │ └── test/java/ # JUnit test in Java │ ├── pom.xml # Maven configuration │ └── build.gradle.kts # Gradle configurationThe
initialmodule contains a simple Todo application in Java with a single test.In the same directory, open your build file and update its contents to support Kotlin:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId> <artifactId>kotlin-junit-complete</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>kotlin-junit-complete</name> <url>https://kotlinlang.org/docs/jvm-test-using-junit.htm</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.release>17</maven.compiler.release> <jexer.version>1.6.0</jexer.version> <kotlin.version>2.3.10</kotlin.version> </properties> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit-bom</artifactId> <version>5.11.0</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- Add JUnit Jupiter engine for test runtime --> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- Optionally: parameterized tests support --> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- Add Kotlin standard library to compile and run Kotlin tests --> <dependency> <groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId> <artifactId>kotlin-stdlib</artifactId> <version>${kotlin.version}</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.gitlab.klamonte</groupId> <artifactId>jexer</artifactId> <version>${jexer.version}</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <pluginManagement><!-- Lock down plugin versions to avoid using Maven defaults (can be moved to a parent pom file) --> <plugins> <!-- Clean lifecycle, see https://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/lifecycles.html#clean_Lifecycle --> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.4.0</version> </plugin> <!-- Default lifecycle, jar packaging: see https://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/default-bindings.html#Plugin_bindings_for_jar_packaging --> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.3.0</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.4.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.1.2</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.1.2</version> </plugin> <!-- Site lifecycle, see https://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/lifecycles.html#site_Lifecycle --> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-site-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.12.1</version> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-project-info-reports-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.6.1</version> </plugin> <!-- No maven-compiler-plugin needed with Kotlin extensions --> </plugins> </pluginManagement> <plugins> <!-- Activate Kotlin Maven plugin for main and test sources --> <plugin> <groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId> <artifactId>kotlin-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${kotlin.version}</version> <extensions>true</extensions> <executions> <execution> <id>default-compile</id> <phase>compile</phase> <configuration> <sourceDirs> <sourceDir>src/main/kotlin</sourceDir> <!-- Ensure Kotlin code can reference Java code --> <sourceDir>src/main/java</sourceDir> </sourceDirs> </configuration> </execution> <execution> <id>default-test-compile</id> <phase>test-compile</phase> <configuration> <sourceDirs> <sourceDir>src/test/kotlin</sourceDir> <sourceDir>src/test/java</sourceDir> </sourceDirs> </configuration> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>In the
<properties>section, set the Kotlin version.In the
<dependencies>section, add JUnit Jupiter dependencies and thekotlin-stdlib(test scope) to compile and run Kotlin tests.In the
<build><plugins>section, applykotlin-maven-pluginwithextensionsenabled and configurecompileandtest-compileexecutions withsourceDirsfor both Kotlin and Java.You don't need to add
maven-compiler-pluginto the<build><pluginManagement>section when using the Kotlin Maven plugin with extensions.
// build.gradle.kts group = "org.jetbrains.kotlin" version = "1.0-SNAPSHOT" description = "kotlin-junit-complete" java.sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17 plugins { application kotlin("jvm") version "2.3.10" } kotlin { jvmToolchain(17) } application { mainClass.set("org.jetbrains.kotlin.junit.App") } repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { implementation("com.gitlab.klamonte:jexer:1.6.0") testImplementation(kotlin("test")) testImplementation(libs.org.junit.jupiter.junit.jupiter.api) testImplementation(libs.org.junit.jupiter.junit.jupiter.params) testRuntimeOnly(libs.org.junit.jupiter.junit.jupiter.engine) testRuntimeOnly(libs.org.junit.platform.junit.platform.launcher) } tasks.test { useJUnitPlatform() }In the
plugins {}block, add thekotlin("jvm")plugin.Set the JVM toolchain version to match your Java version.
In the
dependencies {}block, add thekotlin.testlibrary that provides Kotlin's test utilities and integrates with JUnit.
Kotlin/JVM supports the latest stable JUnit version, JUnit 6. You can find it in the
gradle/libs.versions.tomlversion catalog.If you generally prefer using the version catalog, you can even add the
kotlin("jvm")plugin there:# gradle/libs.versions.toml [versions] kotlin = "2.3.10" junit = "6.0.2" [libraries] org-junit-jupiter-junit-jupiter-api = { module = "org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api", version.ref = "junit" } org-junit-jupiter-junit-jupiter-params = { module = "org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-params", version.ref = "junit" } org-junit-jupiter-junit-jupiter-engine = { module = "org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine", version.ref = "junit" } org-junit-platform-junit-platform-launcher = { module = "org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher" } [plugins] kotlinJvm = { id = "org.jetbrains.kotlin.jvm", version.ref = "kotlin" }Reload the build file in your IDE.
For more detailed instructions on build file setup, see Project configuration.
Add your first Kotlin test
The TodoItemTest.java test in initial/src/test/java already verifies the app basics: item creation, defaults, unique IDs, and state changes.
You can expand the test coverage by adding a Kotlin test that verifies repository-level behavior:
Navigate to the same test source directory,
initial/src/test/java.Create a
TodoRepositoryTest.ktfile in the same package as the Java test.Create the test class with field declarations and setup function:
package org.jetbrains.kotlin.junit import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName internal class TodoRepositoryTest { lateinit var repository: TodoRepository lateinit var testItem1: TodoItem lateinit var testItem2: TodoItem @BeforeEach fun setUp() { repository = TodoRepository() testItem1 = TodoItem("Task 1", "Description 1") testItem2 = TodoItem("Task 2", "Description 2") } }JUnit 5 annotations work the same in Kotlin as in Java.
In Kotlin, the
lateinitkeyword allows declaring non-null properties that are initialized later. This helps to avoid having to use nullable types (TodoRepository?) in your tests.
Add a test inside the
TodoRepositoryTestclass to check the initial repository state and its size:@Test @DisplayName("Should start with empty repository") fun shouldStartEmpty() { Assertions.assertEquals(0, repository.size()) Assertions.assertTrue(repository.all.isEmpty()) }Unlike Java static import, Jupiter's
Assertionsis imported as a class and used as a qualifier for assertion functions.Instead of
.getAll()calls, you can access Java getters as properties in Kotlin withrepository.all.
Write another test to verify copy behavior for all items:
@Test @DisplayName("Should return defensive copy of items") fun shouldReturnDefensiveCopy() { repository.add(testItem1) val items1 = repository.all val items2 = repository.all Assertions.assertNotSame(items1, items2) Assertions.assertThrows( UnsupportedOperationException::class.java ) { items1.clear() } Assertions.assertEquals(1, repository.size()) }To get a Java class object from a Kotlin class, use
::class.java.You can split complex assertions across multiple lines without using any special continuation characters.
Add a test to verify finding items by ID:
@Test @DisplayName("Should find item by ID") fun shouldFindItemById() { repository.add(testItem1) repository.add(testItem2) val found = repository.getById(testItem1.id()) Assertions.assertTrue(found.isPresent) Assertions.assertEquals(testItem1, found.get()) }Kotlin works smoothly with the Java
OptionalAPI. It automatically converts getter methods to properties, that's why theisPresent()method is accessed here as a property.Write a test to verify the item removal mechanism:
@Test @DisplayName("Should remove item by ID") fun shouldRemoveItemById() { repository.add(testItem1) repository.add(testItem2) val removed = repository.remove(testItem1.id()) Assertions.assertTrue(removed) Assertions.assertEquals(1, repository.size()) Assertions.assertTrue(repository.getById(testItem1.id()).isEmpty) Assertions.assertTrue(repository.getById(testItem2.id()).isPresent) } @Test @DisplayName("Should return false when removing non-existent item") fun shouldReturnFalseForNonExistentRemoval() { repository.add(testItem1) val removed = repository.remove("non-existent-id") Assertions.assertFalse(removed) Assertions.assertEquals(1, repository.size()) }In Kotlin, you can chain method calls and property access, for example
repository.getById(id).isEmpty.
Run tests
Run both Java and Kotlin tests to verify your project works as expected:
Run the test using the gutter icon:

You can also run all project tests from the
initialdirectory using the command line:mvn test./gradlew testCheck that the test works correctly by changing one of the variable values. For example, modify the
shouldAddItemtest to expect an incorrect repository size:@Test @DisplayName("Should add item to repository") fun shouldAddItem() { repository.add(testItem1) Assertions.assertEquals(2, repository.size()) // Changed from 1 to 2 Assertions.assertTrue(repository.all.contains(testItem1)) }Run the test again and verify that it fails:
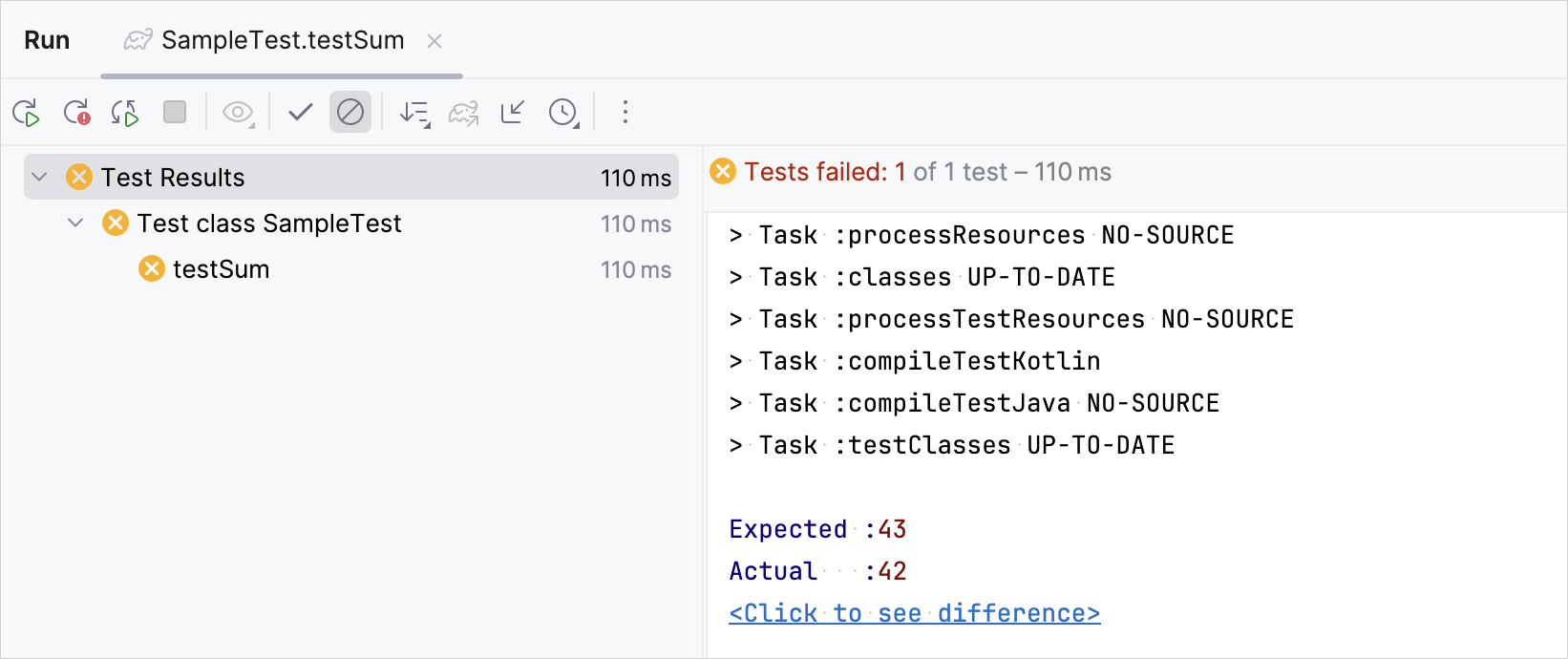
Explore other test libraries
Besides JUnit, you can use other libraries that support both Kotlin and Java:
Library | Description |
|---|---|
Fluent assertion library with chainable assertions. | |
Kotlin wrapper for Mockito that provides helper functions and better integration with Kotlin type system. | |
Native Kotlin mocking library that supports Kotlin-specific features including coroutines and extension functions. | |
Assertion library for Kotlin offering multiple assertion styles and extensive matcher support. | |
Assertion library for Kotlin with type-safe assertions and support for data classes. |
What's next
Improve your test output with the Kotlin's Power-assert compiler plugin.
Create your first server-side application with Kotlin and Spring Boot.
Explore the features of the
kotlin.testlibrary.