Ten reasons to adopt Kotlin Multiplatform and supercharge your projects
In today's diverse tech landscape, developers face the challenge of building applications that can seamlessly operate across various platforms, while optimizing development time and increasing user productivity. Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) offers a solution that allows you to create apps for multiple platforms, facilitating code reuse across them while maintaining the advantages of native programming.
In this article, we'll explore ten reasons why developers should consider using Kotlin Multiplatform in their existing or new projects and why KMP continues to gain a lot of traction.
Adoption is rising steadily: According to the last two Developer Ecosystem surveys, Kotlin Multiplatform usage more than doubled in just a year – increasing from 7% in 2024 to 18% in 2025. This rapid growth highlights the technology’s increasing momentum and the confidence developers place in it.
Why you should try Kotlin Multiplatform in your projects
Whether you're looking to make your development more efficient or explore new technologies, you will find this article helpful. It explains some of the practical benefits of Kotlin Multiplatform, such as streamlining development, supporting multiple platforms, and offering a robust tooling ecosystem. You'll also find case studies from real companies.
Kotlin Multiplatform supports an extensive list of platforms
Kotlin Multiplatform allows for flexible multiplatform development
With the Kotlin Multiplatform solution, you can share UI code
You can use Kotlin Multiplatform in existing and new projects
With Kotlin Multiplatform, you can start sharing your code gradually
Kotlin Multiplatform boasts a large and supportive community
1. Kotlin Multiplatform helps you avoid code duplication
Baidu, the largest Chinese language search engine, launched Wonder App, an application targeted at a younger audience. Here are some of the problems they faced with traditional app development:
Inconsistencies in the app experience: The Android app worked differently from the iOS app.
High cost of verifying the business logic: The work of the iOS and Android developers using the same business logic needed to be independently checked, which led to high costs.
High upgrade and maintenance costs: Duplicating the business logic was complicated and time-consuming, which increased the app's upgrade and maintenance costs.
The Baidu team decided to experiment with Kotlin Multiplatform, starting out by unifying the data layer: data model, RESTful API requests, JSON data parsing, and caching logic.
Then they decided to adopt the Model-View-Intent (MVI) user interface pattern, which allows you to unify the interface logic with Kotlin Multiplatform. They also shared low-level data, the processing logic, and the UI processing logic.
The experiment turned out to be very successful, resulting in the following:
A consistent experience across their Android and iOS apps.
A reduction in their maintenance and testing costs.
Significantly improved productivity within the team.
2. Kotlin Multiplatform supports an extensive list of platforms
One of the key advantages of Kotlin Multiplatform is its extensive support across various platforms, making it a versatile choice for developers. These platforms include Android, iOS, desktop, web (JavaScript and WebAssembly), and server (Java Virtual Machine).
Quizlet, a popular educational platform that aids learning and practice through quizzes, serves as another case study highlighting the benefits of Kotlin Multiplatform. The platform has approximately 50 million active users per month, with 10 million of them on Android. The app ranks inside the top 10 in the education category on Apple's App Store.
The Quizlet team experimented with technologies like JavaScript, React Native, C++, Rust, and Go, but faced various challenges, including performance, stability, and varying implementations across platforms. Finally, they opted for Kotlin Multiplatform for Android, iOS, and web. Here's how using KMP benefited the Quizlet team:
More type-safe APIs when marshaling objects.
25% faster grading algorithm on iOS compared to JavaScript.
Reduced Android app size from 18 MB to 10 MB.
Enhanced developer experience.
Increased interest from team members, including Android, iOS, backend, and web developers, in writing shared code.
3. Kotlin provides simplified code-sharing mechanisms
In the world of programming languages, Kotlin stands out for its pragmatic approach, which means it prioritizes the following features:
Readability over brevity. While concise code is appealing, Kotlin understands that clarity is paramount. The goal isn't just to shorten code but to eliminate unnecessary boilerplate, which enhances readability and maintainability.
Code reuse over sheer expressiveness. It's not just about solving many problems – it's about identifying patterns and creating reusable libraries. By leveraging existing solutions and extracting commonalities, Kotlin enables developers to maximize the efficiency of their code.
Interoperability over originality. Rather than reinventing the wheel, Kotlin embraces compatibility with established languages like Java. This interoperability not only allows seamless integration with the vast Java ecosystem but also facilitates the adoption of proven practices and lessons learned from previous experiences.
Safety and tooling over soundness. Kotlin enables developers to catch errors early, ensuring that your program doesn't fall into an invalid state. By detecting issues during compilation or while writing code in IDEs, Kotlin enhances software reliability, minimizing the risk of runtime errors.
The key takeaway is that Kotlin’s emphasis on readability, reuse, interoperability, and safety makes the language a compelling choice for developers and increases their productivity.
4. Kotlin Multiplatform allows for flexible multiplatform development
With Kotlin Multiplatform, developers no longer need to decide between native and cross-platform development. They can choose what to share and what to write natively.
Before Kotlin Multiplatform, developers had to write everything natively.
Kotlin Multiplatform lets you choose the level of code sharing that works for your project.
Share both logic and UI: For maximum reuse and faster delivery, you can share not only business and presentation logic but also user interface code by combining Kotlin Multiplatform with Compose Multiplatform. This makes it possible to maintain a unified codebase across Android, iOS, desktop, and web while still integrating with platform-specific APIs where needed. This approach helps streamline development and ensures consistent behavior across platforms.
Share logic while keeping a native UI: If platform-specific visual behavior or UX fidelity is a priority, you can choose to share only the data and business logic. With this structure, each platform retains its native UI layer while benefiting from a common, consistent logic implementation. This approach is well-suited for teams that want to reduce duplication without changing their existing UI workflows.
Share a small part of the logic: Kotlin Multiplatform can also be introduced gradually by sharing a focused subset of logic, such as validation, domain calculations, or authentication flows. This option works well when you want to improve consistency and stability across platforms without making large architectural changes.
Now, you can share almost anything, except for platform-specific code.
5. With the Kotlin Multiplatform solution, you can share UI code
JetBrains provides Compose Multiplatform, a declarative framework for sharing user interfaces across multiple platforms, including Android (via Jetpack Compose), iOS, desktop, and web (Beta), based on Kotlin and Jetpack Compose.
Instabee, a last-mile logistics platform specialized for e-commerce businesses, started using Compose Multiplatform in their Android and iOS applications, sharing the UI logic, while the technology was still in its alpha state.
There is an official sample of Compose Multiplatform called ImageViewer App, which runs on Android, iOS, desktop, and web and has integration with native components like maps and the camera. There is also a community sample, the New York Times App clone, which runs even on Wear OS for watches, the smartwatch operating system. Check this list of Kotlin Multiplatform and Compose Multiplatform samples to see more examples.
6. You can use Kotlin Multiplatform in existing and new projects
Let's take a look at the following two scenarios:
Using KMP in an existing project
Once again, there is an example of Wonder App by Baidu. The team already had the Android and iOS apps, and they just unified the logic. They started gradually unifying more libraries and more logic, and then achieved a unified codebase shared across platforms.
Using KMP in a new project
9GAG, an online platform and social media website, tried different technologies, like Flutter and React Native, but finally opted for Kotlin Multiplatform, which allowed them to align the behavior of their app across both platforms. They started by creating an Android app first. Then, they consumed the Kotlin Multiplatform project as a dependency on iOS.
7. With Kotlin Multiplatform, you can start sharing your code gradually
You can begin incrementally, starting with simple elements like constants and gradually migrating common utilities like email validation. You can also write or migrate your business logic, such as transaction processes or user authentication, for instance.
8. Kotlin Multiplatform is already used by global companies
KMP is already used by many large companies all around the world, including Forbes, Philips, Cash App, Meetup, Autodesk, and many others. You can read all of their stories on the case studies page.
In November 2023, JetBrains announced that Kotlin Multiplatform is now Stable, attracting the interest of more companies and teams in the technology. At Google I/O 2024, Google announced official support for using Kotlin Multiplatform to share business logic between Android and iOS.
9. Kotlin Multiplatform provides powerful tooling support
When working with Kotlin Multiplatform projects, you have powerful tooling at your fingertips.
IntelliJ IDEA. With IntelliJ IDEA 2025.2.2, you can install the Kotlin Multiplatform IDE plugin, which offers basic launching and debugging capabilities for iOS apps, preflight environment checks, and other helpful KMP functionality.
Android Studio. Android Studio is another stable solution for Kotlin Multiplatform development. With Android Studio Otter 2025.2.1, you can install the same Kotlin Multiplatform IDE plugin to get basic iOS launching and debugging support, preflight environment checks, and additional multiplatform tooling.
Compose Hot Reload: Compose Hot Reload lets you quickly iterate and experiment with UI changes while working on Compose Multiplatform projects. It is currently available for projects that include a desktop target and are compatible with Java 21 or earlier.
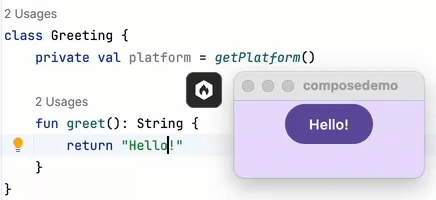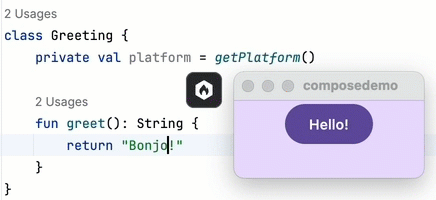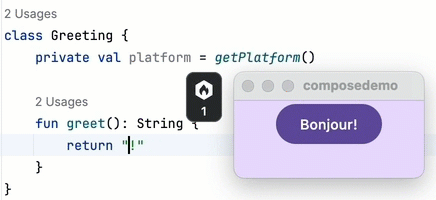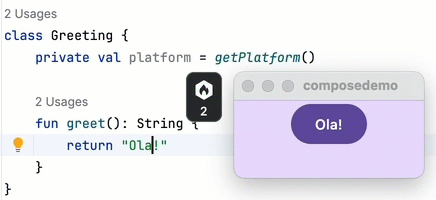
Xcode. Apple's IDE can be used to create the iOS part of Kotlin Multiplatform apps. Xcode is the standard for iOS app development, offering a plethora of tools for coding, debugging, and configuration. However, Xcode is Mac only.
10. Kotlin Multiplatform boasts a large and supportive community
Kotlin and Kotlin Multiplatform have a very supportive community. Here are a few places where you can find answers to any questions you might have.
Kotlinlang Slack workspace. This workspace has about 60,000 members and a few relevant channels dedicated to cross-platform development, like #multiplatform, #compose, and #compose-ios.
Kotlin X. Here, you'll find quick expert insights and the latest news, including myriad multiplatform tips.
Kotlin YouTube. Our YouTube channel provides practical tutorials, livestreams with experts, and other excellent educational content for visual learners.
Kodee's Kotlin Roundup. If you want to stay in the loop with the latest updates across the dynamic Kotlin and Kotlin Multiplatform ecosystems, subscribe to our regular newsletter!
The Kotlin Multiplatform ecosystem is thriving. It's enthusiastically nurtured by numerous Kotlin developers globally. To help the community navigate this expanding landscape, klibs.io provides a curated directory of Kotlin Multiplatform libraries, making it easier to discover reliable solutions for common use cases.
Here is a diagram showing the number of Kotlin Multiplatform libraries created per year:
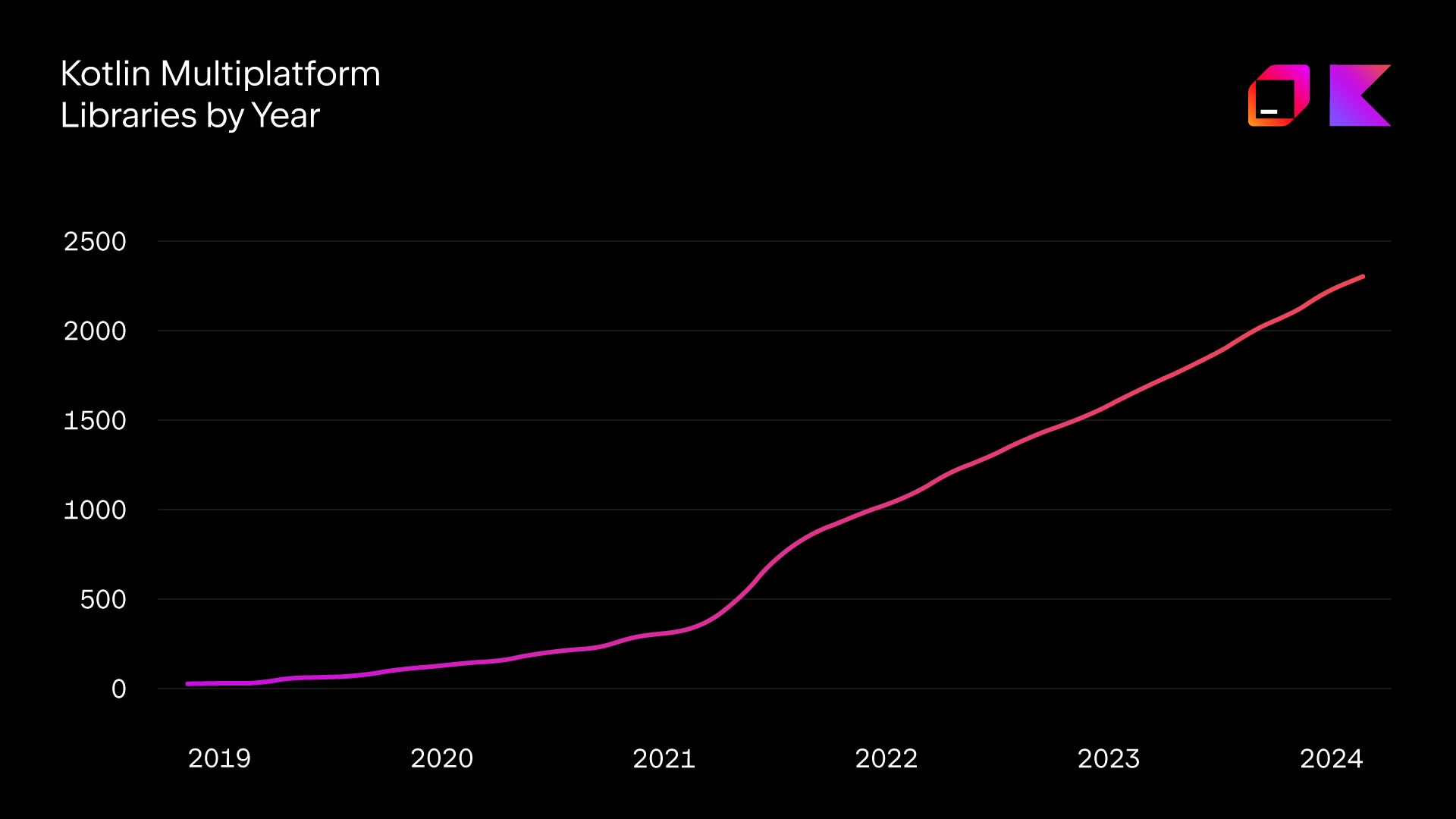
As you can see, there was a definite uptick in 2021, and the number of libraries hasn't stopped growing since.
Why choose Kotlin Multiplatform over other cross-platform technologies?
When choosing between different cross-platform solutions, it's essential to weigh up both their advantages and disadvantages. You can also explore side-by-side comparisons of Kotlin Multiplatform with other technologies, including React Native and Flutter.
Here's a breakdown of the key reasons why Kotlin Multiplatform might be the right choice for you:
Excellent tooling, easy to use. Kotlin Multiplatform leverages Kotlin, offering excellent tooling and ease of use for developers.
Native programming. It's easy to write things natively. Thanks to the expected and actual declarations, you can enable your multiplatform app to access platform-specific APIs.
Great cross-platform performance. Shared code written in Kotlin is compiled into different output formats for different targets: Java bytecode for Android and native binaries for iOS, ensuring good performance across all platforms.
AI-powered code generation. You can speed up multiplatform development with code generation powered by Junie, the JetBrains coding agent that supports a more efficient workflow across shared and platform-specific code.
If you've already decided to try Kotlin Multiplatform, here are a few tips that will help you get started:
Start small. Begin with small shared components or constants to familiarize the team with the workflow and benefits of Kotlin Multiplatform.
Create a plan. Develop a clear experiment plan, hypothesizing the expected outcomes and methods for implementation and analysis. Define roles for contributing to shared code and establish workflows for distributing changes effectively.
Evaluate and run a retrospective. Run a retrospective meeting with your team to assess the experiment's success and identify any challenges or areas for improvement. If it worked for you, you might want to expand the scope and share even more code. If not, you need to understand the reasons why this experiment didn't work out.
For those who want to help their team get started with Kotlin Multiplatform, we prepared a detailed guide with practical tips.
As you can see, Kotlin Multiplatform is already being successfully used by many massive companies to build high-performance cross-platform applications with native-looking UIs, effectively reusing code across them, while maintaining the benefits of native programming.