Using multiplatform resources in your app
When you've set up the resources for your project, build the project to generate the special Res class which provides access to resources. To regenerate the Res class and all the resource accessors, build the project again or re-import the project in the IDE.
After that, you can use the generated class to access the configured multiplatform resources from your code or from external libraries.
Read on for details about the following topics:
Customizing the accessor class generation: how to make it public, assign to a package, or generate it unconditionally.
Working with specific resource types:
Drawable resources, such as simple images, rasterized images, or XML vectors,
Vector Android XML icons from the Material Symbols library,
Strings, including simple strings, templates, arrays, and plurals,
Raw files and converting byte arrays into images.
Handling web-specific resources:
Preloading of resources using browser features and the preload API,
Working with external resources: from external libraries, remote files, and Java resources.
Importing the generated class
To use the prepared resources, import the generated class, for example:
Here:
projectis the name of your projectcomposeappis the module where you placed the resource directoriesResis the default name for the generated classexample_imageis the name of an image file in thecomposeResources/drawabledirectory (example_image.png, for example).
Customizing accessor class generation
You can customize the generated Res class to suit your needs using Gradle settings.
In the compose.resources {} block of the build.gradle.kts file, you can specify several settings that affect the way the Res class is generated for your project. An example configuration looks like this:
publicResClassset totruemakes the generatedResclass public. By default, the generated class is internal.packageOfResClassallows you to assign the generatedResclass to a particular package (to access within the code, as well as for isolation in a final artifact). By default, Compose Multiplatform assigns the{group name}.{module name}.generated.resourcespackage to the class.generateResClassset toalwaysmakes the project unconditionally generate theResclass. This may be useful when the resource library is only available transitively. By default, Compose Multiplatform uses theautovalue to generate theResclass only if the current project has an explicitimplementationorapidependency on the resource library.
Resource usage
Images
You can access drawable resources as simple images, rasterized images or XML vectors. SVG images are supported on all platforms except Android.
To access drawable resources as
Painterimages, use thepainterResource()function:@Composable fun painterResource(resource: DrawableResource): Painter {...}The
painterResource()function takes a resource path and returns aPaintervalue. The function works synchronously on all targets except for web. For the web target, it returns an emptyPainterfor the first recomposition that is replaced with the loaded image in subsequent recompositions.painterResource()loads either aBitmapPainterfor rasterized image formats, such as.png,.jpg,.bmp,.webp, or aVectorPainterfor the Android XML vector drawable format.XML vector drawables have the same format as Android, except that they don't support external references to Android resources.
To access drawable resources as an
ImageBitmaprasterized image, use theimageResource()function:@Composable fun imageResource(resource: DrawableResource): ImageBitmap {...}To access drawable resources as an
ImageVectorXML vector, use thevectorResource()function:@Composable fun vectorResource(resource: DrawableResource): ImageVector {...}
Here's an example of how you can access images in your Compose Multiplatform code:
Icons
You can use the vector Android XML icons from the Material Symbols library:
Open the Google Fonts Icons gallery, choose an icon, go to the Android tab, and click Download.
Add the downloaded XML icon file to the
drawabledirectory of your multiplatform resources.Open the XML icon file and set
android:fillColorto#000000. Remove any other Android-specific attributes for color adjustments likeandroid:tint.Before:
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="24dp" android:height="24dp" android:viewportWidth="960" android:viewportHeight="960" android:tint="?attr/colorControlNormal"> <path android:fillColor="@android:color/white" android:pathData="..."/> </vector>After:
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="24dp" android:height="24dp" android:viewportWidth="960" android:viewportHeight="960"> <path android:fillColor="#000000" android:pathData="..."/> </vector>Build the project to generate the resource accessors, or let the Kotlin Multiplatform IDE plugin handle it automatically.
Here's an example of how you can access an icon and adjust the colors using the colorFilter parameter in your Compose Multiplatform code:
Strings
Store all string resources in XML files in composeResources/values directories. A static accessor is generated for each item in each file.
Compose Multiplatform supports an Emmet-like shorthand syntax for adding string resources, string arrays, and plurals directly in XML files. For example, when you type test{Example} or s.test{Example} in strings.xml and press Tab, it will automatically expand into <string name="test">Example</string>.
To learn how to localize strings for different locales, refer to the guide on localizing strings.
Simple strings
To store a simple string, add a <string> element to your XML:
To get string resources as a String, use the following code:
For example:
For example:
You can use special symbols in string resources:
\n– for a new line\t– for a tab symbol\uXXXX– for a specific Unicode character
You don't need to escape special XML characters like "@" or "?" as you do for Android strings.
String templates
Currently, arguments have basic support for string resources. When creating a template, use the %<number> format to place arguments within the string and include a $d or $s suffix to indicate that it is a variable placeholder and not simple text. For example:
After creating and importing the string template resource, you can refer to it while passing the arguments for placeholders in the correct order:
There is no difference between the $s and $d suffixes, and no others are supported. You can put the %1$s placeholder in the resource string and use it to display a fractional number, for example:
String arrays
You can group related strings into an array and automatically access them as a List<String> object:
To get the corresponding list, use the following code:
For example:
For example:
Plurals
When your UI displays quantities of something, you might want to support grammatical agreement for different numbers of the same thing (one book, many books, and so on) without creating programmatically unrelated strings.
The concept and base implementation in Compose Multiplatform are the same as for quantity strings on Android. See the Android documentation for more about best practices and nuances of using plurals in your project.
The supported variants are
zero,one,two,few,many, andother. Note that not all variants are even considered for every language: for example,zerois ignored for English because it is the same as any other plural except 1. Rely on a language specialist to know what distinctions the language actually insists upon.It's often possible to avoid quantity strings by using quantity-neutral formulations such as "Books: 1". If this doesn't worsen the user experience,
To define a plural, add a <plurals> element to any .xml file in your composeResources/values directory. A plurals collection is a simple resource referenced using the name attribute (not the name of the XML file). As such, you can combine plurals resources with other simple resources in one XML file under one <resources> element:
To access a plural as a String, use the following code:
For example:
For example:
Fonts
Store custom fonts in the composeResources/font directory as *.ttf or *.otf files.
To load a font as a Font type, use the Font() composable function:
For example:
To support special characters like emojis or Arabic script in web targets, you need to add the corresponding fonts to resources and preload fallback fonts.
Raw files
To load any raw file as a byte array, use the Res.readBytes(path) function:
You can place raw files in the composeResources/files directory and create any hierarchy inside it.
For example, to access raw files, use the following code:
Convert byte arrays into images
If the file you are reading is a bitmap (JPEG, PNG, BMP, WEBP) or an XML vector image, you can use the following functions to convert them into ImageBitmap or ImageVector objects suitable for the Image() composable.
Access the raw files as shown in the Raw files section, then pass the result to a composable:
On every platform except Android, you can also turn an SVG file into a Painter object:
Generated maps for resources and string IDs
For ease of access, Compose Multiplatform also maps resources with string IDs. You can access them by using the filename as the key:
An example of passing a mapped resource to a composable:
Compose Multiplatform resources as Android assets
Starting with Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0, all multiplatform resources are packed into Android assets. This enables Android Studio to generate previews for Compose Multiplatform composables in Android source sets.
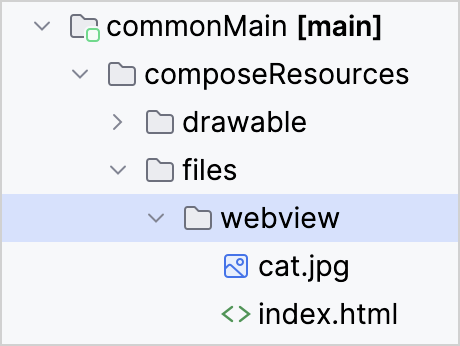
Using Multiplatform resources as Android assets also makes possible direct access from WebViews and media player components on Android, since resources can be reached by a simple path, for example Res.getUri("files/index.html").
An example of an Android composable displaying a resource HTML page with a link to a resource image:
The example works with this simple HTML file:
Both resource files in this example are located in the commonMain source set:
Interaction with other libraries and resources
Accessing multiplatform resources from external libraries
If you want to process multiplatform resources using other libraries included in your project, you can pass platform-specific file paths to these other APIs. To get a platform-specific path, call the Res.getUri() function with the project path to the resource:
Now that the uri variable contains the absolute path to the file, any external library can use that path to access the file in a manner that suits it.
For Android-specific uses, multiplatform resources are also packed as Android assets.
Remote files
In the context of the resource library, only files that are part of the application are considered resources.
You can load remote files from the internet using their URL using specialized libraries:
Using Java resources
While you can use Java resources with Compose Multiplatform, they don't benefit from extended features provided by the framework: generated accessors, multimodule support, localization, and so on. Consider transitioning fully to the multiplatform resource library to unlock that potential.
With Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0, the resources API available in the compose.ui package is deprecated. If you still need to work with Java resources, copy the following implementation to your project to ensure that your code works after you upgrade to Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0 or above:
What's next?
Check out the official demo project that shows how resources can be handled in a Compose Multiplatform project targeting iOS, Android, and desktop.
Learn how to manage the application's resource environment like in-app theme and language.